The Solar System
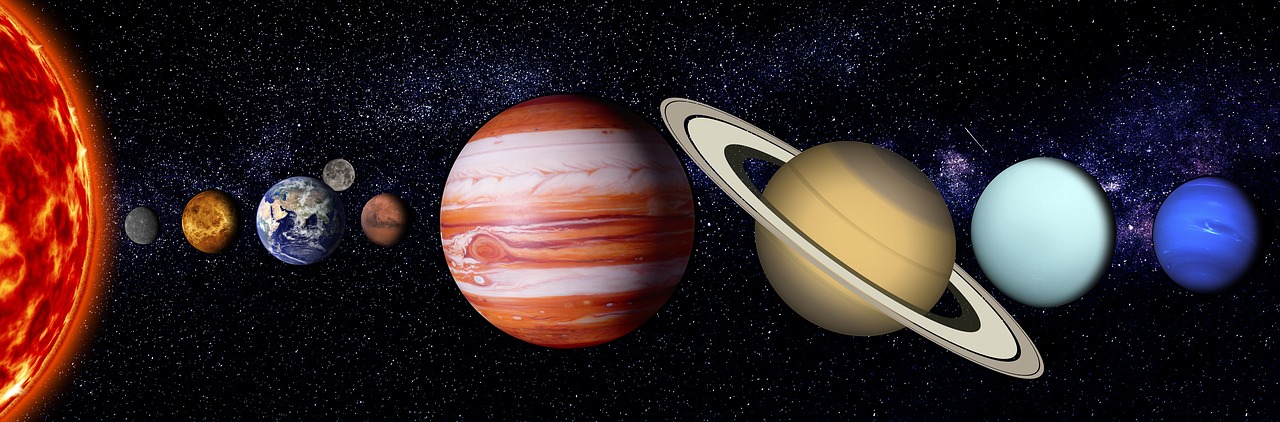
We know that the Sun is the host star of our solar system and that eight planets and other objects such as dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets orbit the Sun. In addition, some of the planets have moon(s) and rings orbiting around them.
But have you ever thought about these questions?
- Why is our solar system called so?
- What happened to Pluto, the nineth planet once? Why isn’t it a planet anymore? What is it then?
- Though the planet Mercury is the closest to the Sun, it is not the hottest planet. Which one is the hottest planet then?
- Have you ever heard of the Sun rising in the west? It happens on a couple of planets in the solar system. Which are they?
- On a couple of planets, their days are longer than their years. Which are these planets?
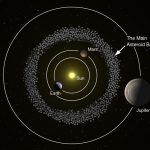
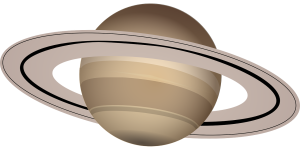
- Saturn has a spectacular ring system. But have you ever wondered what these rings are made of?
- How has the Sun able to shine for last 4.6 billion years producing so much energy? What is the process that is creating so much energy? How long is it going to last?
- Is there life, or any signs for the past existence of life, on any other planet or object in the solar system?
- What was the event, happened on earth 65 million years ago, that made dinosaurs completely extinct? Can it happen again?
Curious to explore our amazing solar system? Let us find out the meaning of ‘solar’, first.
What does Solar mean?
A planetary system consists of several planets revolving around a host star or a couple of host stars (as is commonly the case). The Sun is the lone host star of our planetary system. In Greek, the word ‘Solis’ refers to the Sun. Therefore, our planetary system is known as solar system. And anything related to the Sun is solar.
Our host star the Sun is a medium-sized star, and it is one of the 100 billion or more stars in our Milky Way galaxy. As per an estimate, the universe may contain two trillion such galaxies!!
Origin of Solar System
Nebular Hypothesis
Our solar system formed about 4.6 billion years ago from interstellar gas. This interstellar gas, over a lengthy period of time, clumped together to form a disk of rotating solar nebula. When the solar nebula collapsed to its center due to gravity, the center of the nebula became so dense and so hot that nuclear fusion got ignited. And the Sun was born.
The remaining rotating islands of clouds coalesced to form the planets around the Sun. Heavier content of the clouds withstood the solar wind and heat from the Sun and stayed in the inner orbits while the gaseous part of the cloud got pushed to the outer orbits. Therefore, the solar system has rocky terrestrial planets with metallic core in orbits closer to the Sun while the gaseous giant planets are far away from the Sun.
Here are a few key evidences that support the nebular hypothesis:
- Orbits of all the planets are in the same plane.
- The equator of Sun’s rotation coincides with the plane of the orbits of the planets.
- All planets are orbiting the Sun in the same direction as that of the rotation of the Sun.
Interesting Facts
- Sun, the star of our solar system, is one of the 100 billion stars in our home galaxy Milky Way.
- Diameter of Milky Way is 100,000 lightyears. As you may know, light travels 300,000 Kilometers per second in vacuum. One lightyear is the distance that light travels in a year. When we do the math (of one lightyear = 300000*365.25 * 24* 60*60), we will get 9.462 trillion Kilometers!!
- The closest star to Earth, other than our Sun, is Proxima Centauri which is 4.4 lightyears away from our earth.
- All the stars that we see in a beautiful night sky are all in the Milky Way galaxy.
- Our solar system is located 28,000 lightyears from the center of Milky Way.
- The whole solar system orbits the center of the Milky Way in 230 million years.
- Here is the list how we travel in space, but we never feel it:
- Earth is rotating on its axis and completes one rotation in 24 hours.
- At the same time, earth is orbiting the Sun and completes an orbit in 365.25 days.
- The Sun is not stationary. It is orbiting the center of Milky Way and completes one galactic orbit in 230 million years.
- And the Milky Way is not stationary either. It is heading towards our neighboring Andromeda galaxy which is 2.5 million lightyears away.
Click on the pictures below to read more on them.
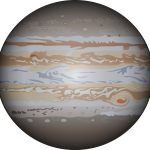
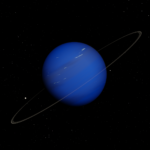
Planets
Ready to take a Quiz on Solar System now?
Sources:
Information and data, in this post, are based on the following sources:
- https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/solar-system/our-solar-system
- The Cambridge Guide to the Solar System By Kenneth R. Lang, Cambridge University Press.